State Machine Lesson
What is a State Machine?
Definitions
- Technical Definition: An abstract model to outline sequential logic.
- Conceptual Definition: Think of it as a "map of choices" that are dependent on previous choices.
Core Concepts
- State: Essentially represents a condition or a set of conditions.
- Transition: If the condition or state changes, it results in a transition to the next state.
Examples of State Machines
1. Simple Example: Traffic Lights
In this example, the colors are the states.
stateDiagram-v2
direction LR
%% States
Green
Yellow
Red
%% Transitions
Green --> Yellow : 60 Seconds
Yellow --> Red : 60 Seconds
Red --> Green : 60 Seconds
%% Styling
style Green fill:#90EE90
style Yellow fill:#FFFF00
style Red fill:#FF6B6BThe Logic Flow:
- After 60 seconds: 🟢 Green transitions to 🟡 Yellow.
- After an additional 60 seconds: 🟡 Yellow goes to 🔴 Red.
- After 60 more seconds: 🔴 Red goes to 🟢 Green.
Constraints:
- 🟢 Green cannot directly transition to 🔴 Red.
- 🔴 Red cannot directly transition to 🟡 Yellow.
2. Complex Example: Super Mario
In this example, Mario's forms are the states and the items are the conditions for transitioning.
stateDiagram-v2
direction LR
%% States
state "🔴 Mario" as M
state "🔴➡️🔵 Super Mario" as SM
state "🔴➡️🔥 Fire Mario" as FM
state "🔴➡️🪶 Cape Mario" as CM
%% Transitions based on Items (Conditions)
M --> SM : 🍄 Mushroom
SM --> FM : 🔥 Fire Flower
SM --> CM : 🪶 Feather
%% Cross Transitions
FM --> CM : 🪶 Feather
CM --> FM : 🔥 Fire Flower
%% Styling
style M fill:#FF6B6B,color:#fff
style SM fill:#4A90E2,color:#fff
style FM fill:#FFB347,color:#000
style CM fill:#90EE90,color:#000The Logic Flow:
- One state can transition to several other states depending on the conditions.
- Normal Mario has three different states he can transition to depending on the item he collects.
- The other states can transition to one another depending on the item.
- The diagram maps all the transitions Mario can make.
Why Use a State Machine?
- Reliable: It is reliable and intelligent.
- Automated Thinking: The code does the thinking for you.
- Abstraction: Allows you to approach programming from a high-level/abstract perspective.
- Structure: Think of code as step-by-step logic.
Case Study: 2024 Offbot State Machine
This diagram shows a real-world application used by Team 3255.
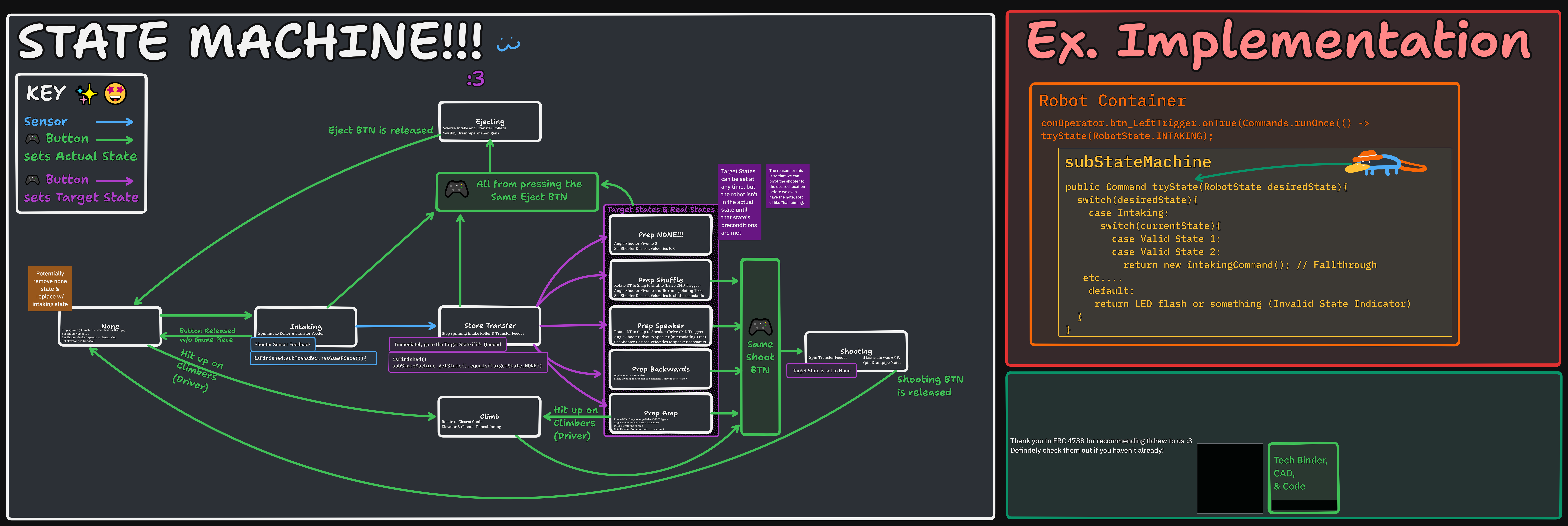
Key Mechanics:
- Target States: Can be set at any time (via buttons), but the robot remains in the actual state until that state's preconditions are met.
- Flow Example:
- Intaking: Transitions to "Store Transfer" when sensor feedback confirms it is finished.
- Store Transfer: Can branch into various "Prep" states (Speaker, Shuffle, Amp) based on inputs.
- Shooting: Triggered when the "Same Shoot BTN" is pressed.
- Climb: Triggered by the driver hitting "up on Climbers".
Implementation Guide
How to Implement a State Machine
Important
States are the goal that the robot is trying to achieve
- List States: Before programming, list the states.
- Identify Motors: Identify all motors/counts
- Categorize Motors: Decide what type of motor it is. Does it go in Motion or Rotors?
- Connect the motors: Identify which motors are involved in each state.
- Create Issues for Clustered Motors/States: Split the motors/states by Rotors and Motion to avoid merge conflicts.
- Assign and Implement Issues to Create Protobot Skeleton
- Assign Buttons: Assign buttons to trigger state transitions.
- Identify Conditions: Identify transition conditions, including inputs.
- Create Diagram: Create a diagram of the states and transitions to show how the completion of one command leads to the next.